Gender and gender re-assignment
- Gender equality in the NHS
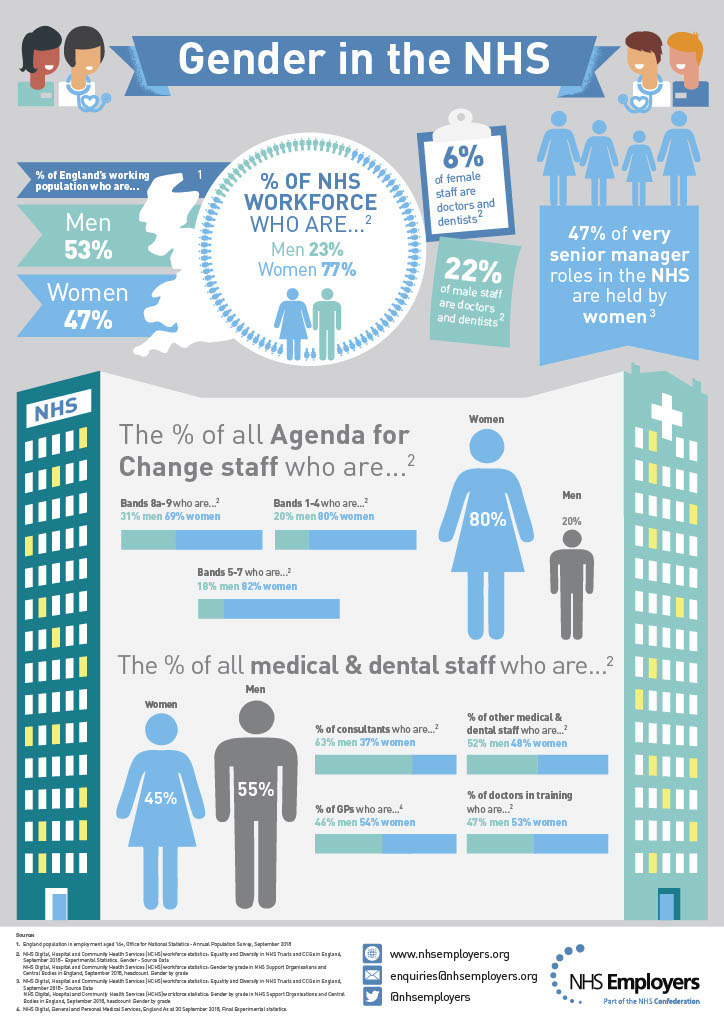
Around one million women work for the NHS in England, making it one of the largest employers of women in the world. However, despite making up the majority of the NHS workforce, women are more likely than men to face structural constraints within the workplace, are paid less, are less likely to get promoted and less likely to be represented in senior roles within the NHS.
- Equal pay and gender pay gap reporting
Equal pay and gender pay are different. Equal pay relates to men and women being paid the same for the same work or work of equal value. Gender pay is the difference in the gross hourly earnings for all employed men, compared to all women. However, the requirement to report on the gender pay gap has focused minds around pay equality.
The majority of NHS staff fall under the Agenda for Change pay system, which has been tested in the courts and found to be equality- proofed at national level. However, there is still considerable risk at local level should procedures not be adhered to.
Since 2017, all organisations in the UK with more than 250 employees, including NHS organisations, have been required to publish details of their gender pay gap figures as well their action plans for closing their gap by the end of the financial year.
- Gender pay gap reporting
As part of gender pay gap reporting, employers are required to report on six measures that show the difference in average earnings between men and women across an organisation or the labour market. The figures are expressed as a percentage of men’s earnings and include:
- mean gender pay gap in hourly pay
- median gender pay gap in hourly pay
- mean bonus gender pay gap
- median bonus gender pay gap
- proportion of men and women receiving a bonus payment
- proportion of men and women in each pay quartile.
